Atmospheric Pollution Control AM216021 Current Open for UCT
Topic outline
-
General information
 This course provides fundamental knowledge in the nature of atmospheric pollution, relative types, correlated effects, control principles and applications.
This course provides fundamental knowledge in the nature of atmospheric pollution, relative types, correlated effects, control principles and applications.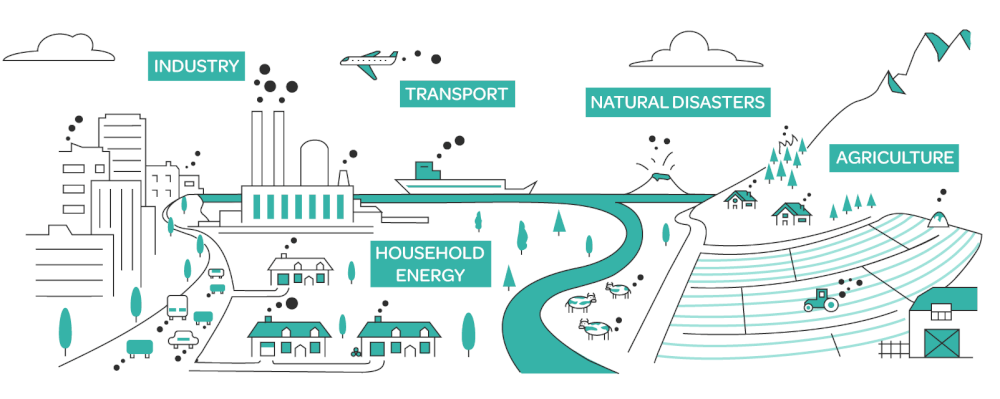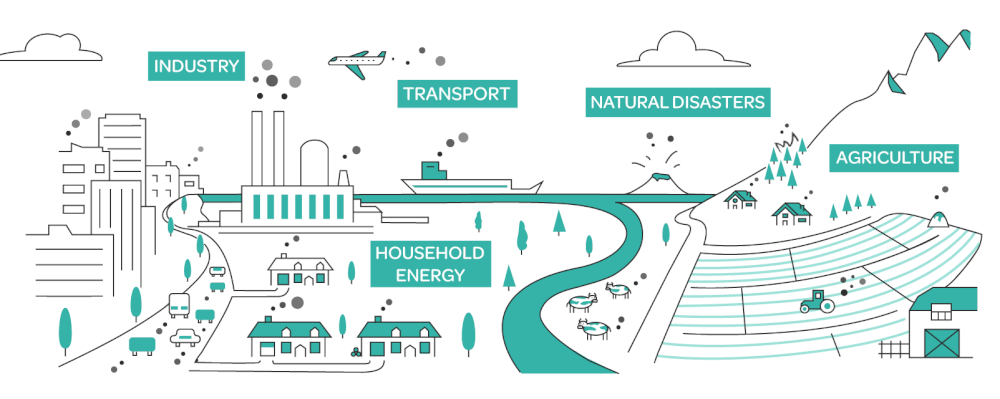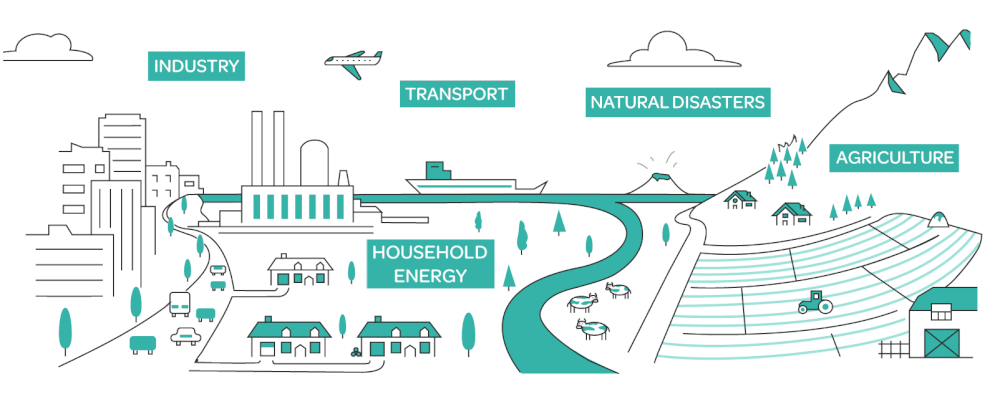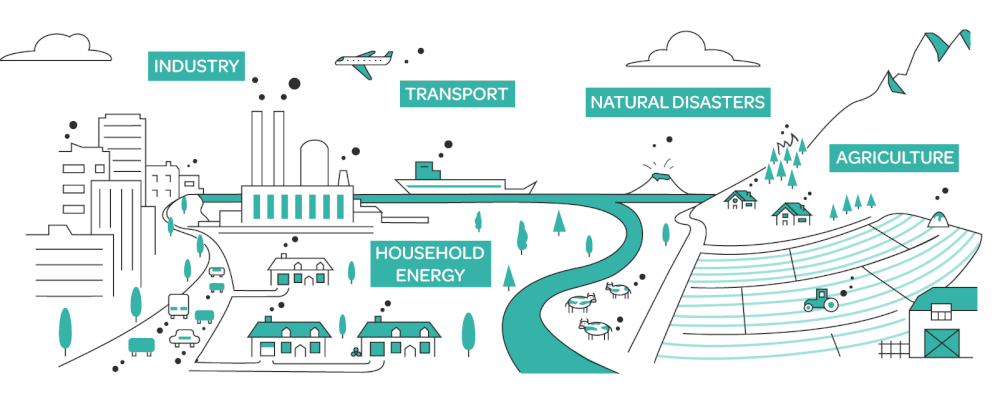
The interactive video conferencing-based tools are available in Microsoft Teams and Zoom Video Communications (screen share interactive face-to-face learning).


-
Extra information associated with a particular point in a document or other piece of information
-
Contact, profile, and consultancy tools with the professor
-
General principles, pedagogy and management strategies used for classroom instruction
-
Types and grades of qualification suggested to follow the course
-
Resources used in teaching and learning to help achieve desired studying objectives
-
The amount of working time expected or assigned students
-
General endpoints of knowledge and understanding after the study
-
Function indicates that the study should completed with substantially quality and credit
-
Assessment by lecturer of all aspects of the learning experience
-
Recommended textbooks, reference books, workbooks and handbooks
-

An informal gathering where current students can learn all about
(designed openly for enrolled participants)
-
-
-
Lecture 14. Meteorological considerations on transport and dispersion of air pollutants Lesson
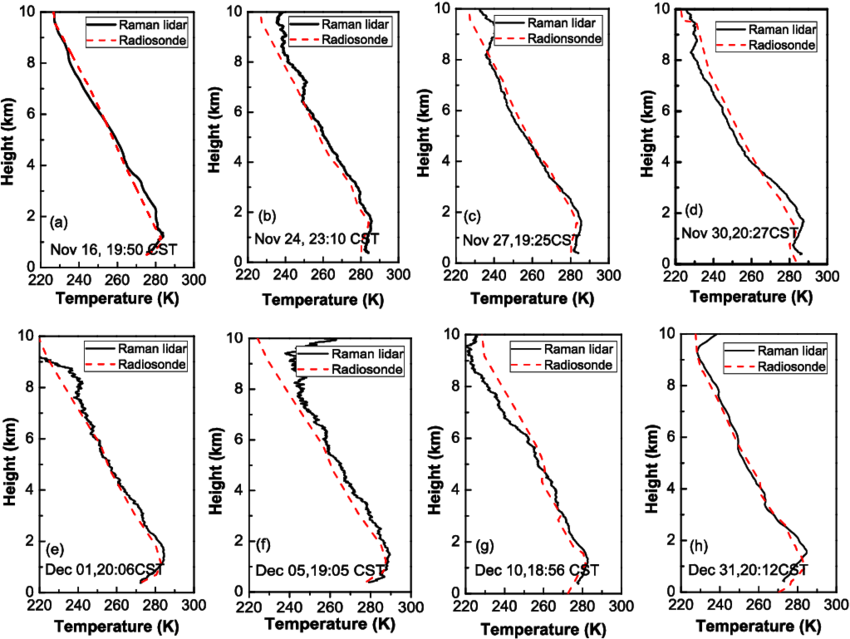
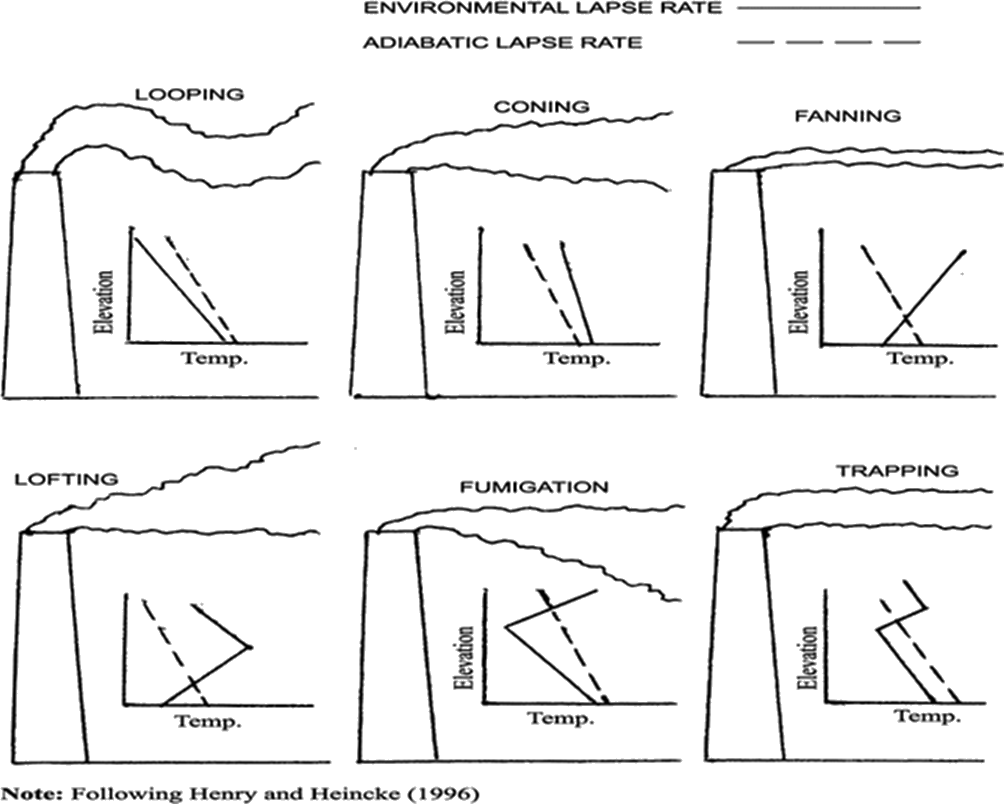
Key issues:
- Affected: winds & temperatures profiles, cloud, humidity
- Large‐scale system: high & low pressure
- Small‐scale system: temperatures, moisture
- Forces: acting on air, combination to form winds
- Winds: global, regional, and local circulations
- Effects on air pollution: stability, mixing, build‐up, clean‐out
- Effects on local air pollution: heating, topography, turbulence
- Specific issues of urban heat island, street canyon, breeze cells
-
Module 14. Meteorological considerations on transport and dispersion of air pollutants File PDF
(Supporting handouts for Lecture 14, printable pdf format, A4 size, landscape layout)
6.5 MB -
Shared media: visualization of large-scale weather patterns, global circulations, climate cells and zones Page
Illustrative video clips:
- Global circulations influence the wind patterns and jet streams
- Climate cells and zones, El Niño and La Nina
- Large-scale weather patterns by simulated CO2 circulation in a year
- Air pollution trapped by mist, fog, haze, layers of cloud, rain or drizzle caused by inversions
- Shifting wind patterns, weather extremes, and vicious cycle in accelerating climate change
-
Relevant link / literature URL
NOAA - Real-time Environmental Applications and Display system

-
Individual presentation 14 Workshop
Title 14: Global stratospheric ozone layer depletion
-
Practical exercise series / Topics 28 and 29 Assignment

Topic 28. Characteristics of stack plumes, 6pts
(a. 2pts / b. 2pts / c. 2pts)Topic 29. Turbulence and mixing process, 6pts
(a. 3pts / b. 3pts)
-
