14. Meteorological considerations on transport and dispersion of air pollutants AM216021 Latest Open for UCT
Section outline
-
-
Lecture 14. Meteorological considerations on transport and dispersion of air pollutants Lesson
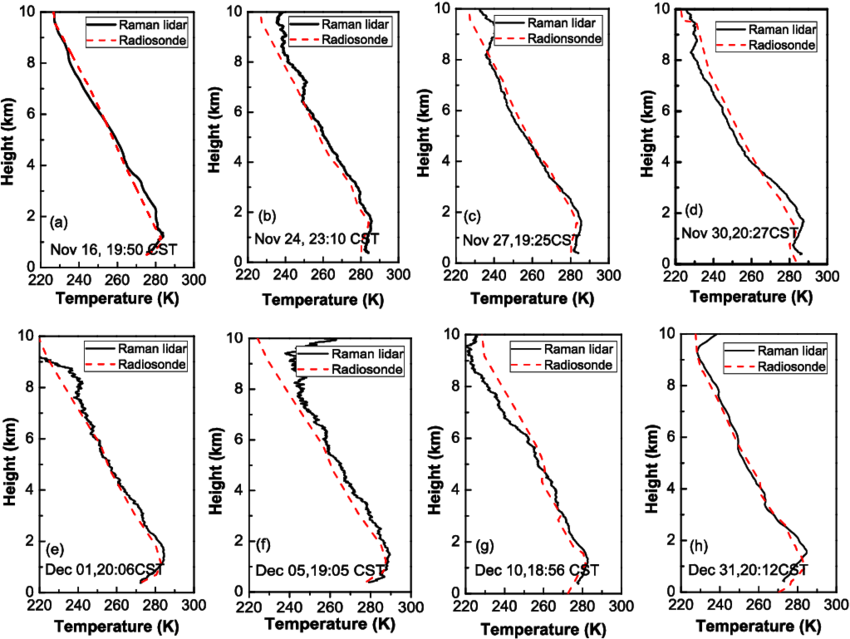
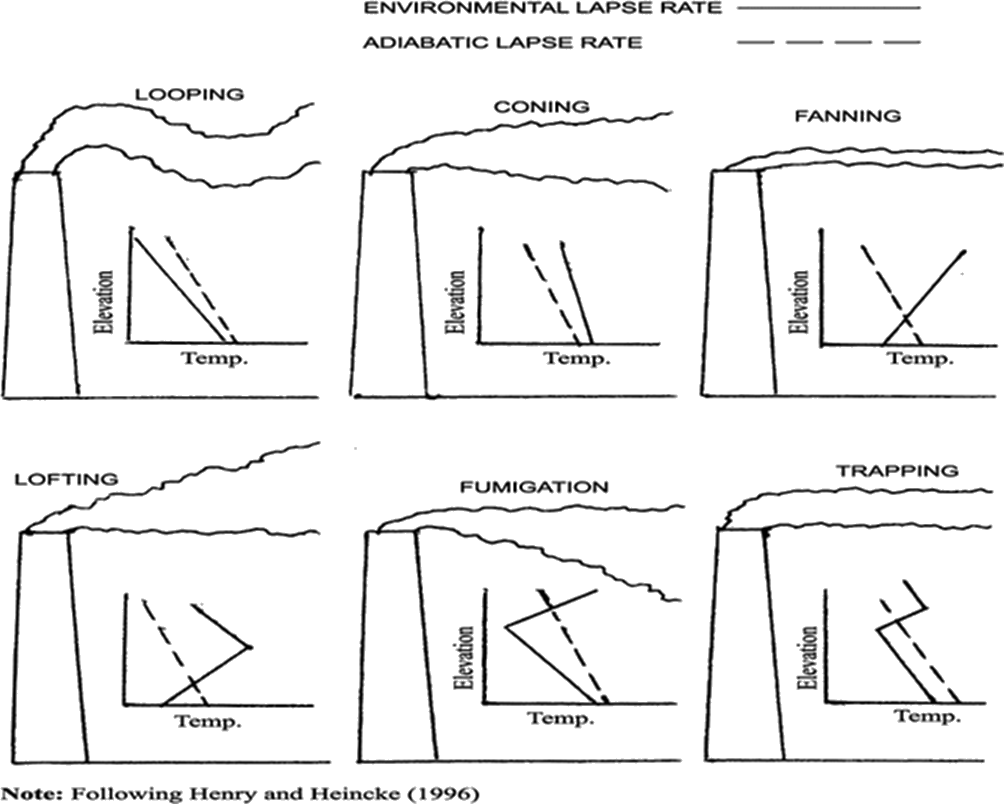
Key issues:
- Affected: winds & temperatures profiles, cloud, humidity
- Large‐scale system: high & low pressure
- Small‐scale system: temperatures, moisture
- Forces: acting on air, combination to form winds
- Winds: global, regional, and local circulations
- Effects on air pollution: stability, mixing, build‐up, clean‐out
- Effects on local air pollution: heating, topography, turbulence
- Specific issues of urban heat island, street canyon, breeze cells
-
Module 14. Meteorological considerations on transport and dispersion of air pollutants File PDF

Supporting handouts for Lecture 14,
Printable pdf format, A4 size, landscape layout6.5 MB -
Shared media: visualization of large-scale weather patterns, global circulations, climate cells and zones Page
Illustrative video clips:
- Global circulations influence the wind patterns and jet streams
- Climate cells and zones, El Niño and La Nina
- Large-scale weather patterns by simulated CO2 circulation in a year
- Air pollution trapped by mist, fog, haze, layers of cloud, rain or drizzle caused by inversions
- Shifting wind patterns, weather extremes, and vicious cycle in accelerating climate change
-
Relevant link / literature URL
NOAA - Real-time Environmental Applications and Display system

-
Individual presentation 14 Forum

Title 14 Global stratospheric ozone layer depletion
-
Practical exercise series / Topics 28 and 29 Assignment

Topic 28. Characteristics of stack plumes, 6pts
(a. 2pts / b. 2pts / c. 2pts)Topic 29. Turbulence and mixing process, 6pts
(a. 3pts / b. 3pts)
-