12. Indoor air pollution, syndrome, health effects and control AM216021 Latest Open for UCT
Section outline
-
-
Lecture 12: Indoor air pollution, syndrome, health effects and control Lesson
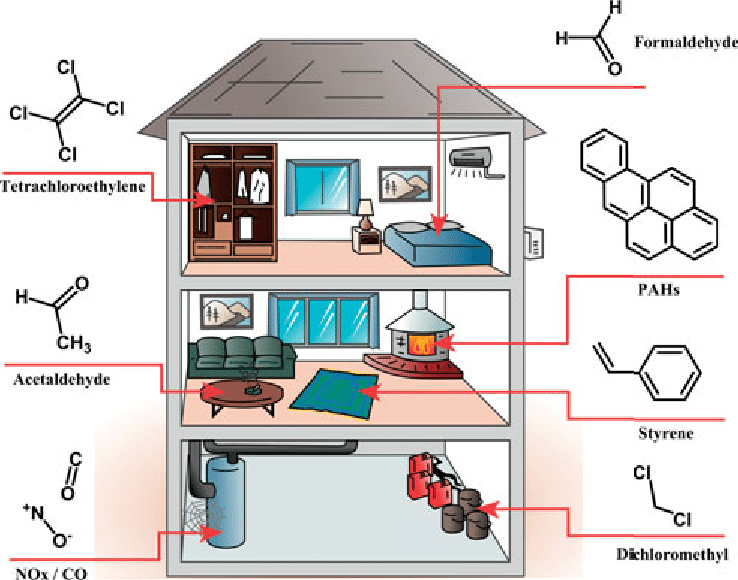
Key issues:
Significant impact on human health risk
Contains many of the same pollutants as outdoor air, also contains VOCs, allergens, fungi, bacteria and viruses
Pollution concentrations usually differ in mixing ratios:- O3 and SO2 are usually less
- Formaldehydes are usually greater
- CO, NOx are generally the same or less
- Radon, asbestos and ETS, when present, are usually greater
Regulated only in the workplace and in public buildings. Residential air is not properly regulated.
-
Module 12. Indoor air pollution and control File PDF

Supporting handouts for Lecture 12
Printable pdf format, A4 size, landscape layout4.6 MB -
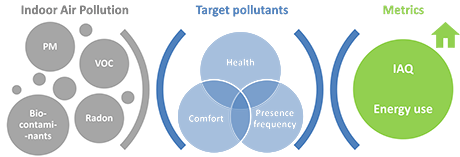
Shared media: potential indoor air quality issues Page
Illustrative video clips:
+ Five concerned levels of indoor air pollutants
+ Cabin-air circulation in the aircraft inlet/outlet
+ Indoor air exchange/ventilation mechanism
+ Turbulence, flows, plumes around the human body -
Relevant link / literature URL
EPA - Indoor pollutants and sources
-
Individual presentation 12 Forum

Title 12: Indoor air, odour and noise pollution, effects and control
-
Practical exercise series / Topics 25, 26 and 27 Assignment

Topic 25. Indoor gaseous pollutant, 5pts
(a. 1 pt / b. 1 pt / c. 1 pt / d. 1 pt / e. 1 pt)
Topic 26. Indoor aerosol particle concentration, 3pts
(a. 1 pt / b. 1 pt / c. 1 pt)
Topic 27. Environmental Tobacco Smoke, 4pts
(a. 2 pts / b. 1 pt / c. 1 pt)
-